Bruce Power operations staff synchronizes Unit 6 to the Ontario electrical grid on September 8. (Photo: Bruce Power)
The ongoing major component replacement (MCR) project at Ontario’s Bruce nuclear power plant reached another milestone last Friday with the reconnection to the grid of the facility’s Unit 6 reactor. According to a release from plant operator Bruce Power, the work was completed ahead of schedule and on budget despite the challenges of the COVID-19 pandemic.
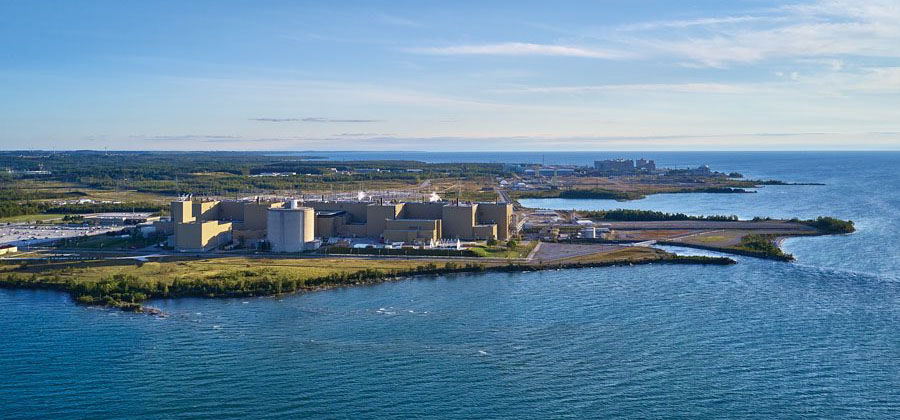
The Bruce nuclear power plant in Ontario, Canada. (Photo: Bruce Power)
Unit 6 at the Bruce nuclear power plant in Kincardine, Ontario, achieved a sustained fission chain reaction over the weekend—a key step in returning the 817-MWe CANDU reactor to commercial operation, Bruce Power announced yesterday.
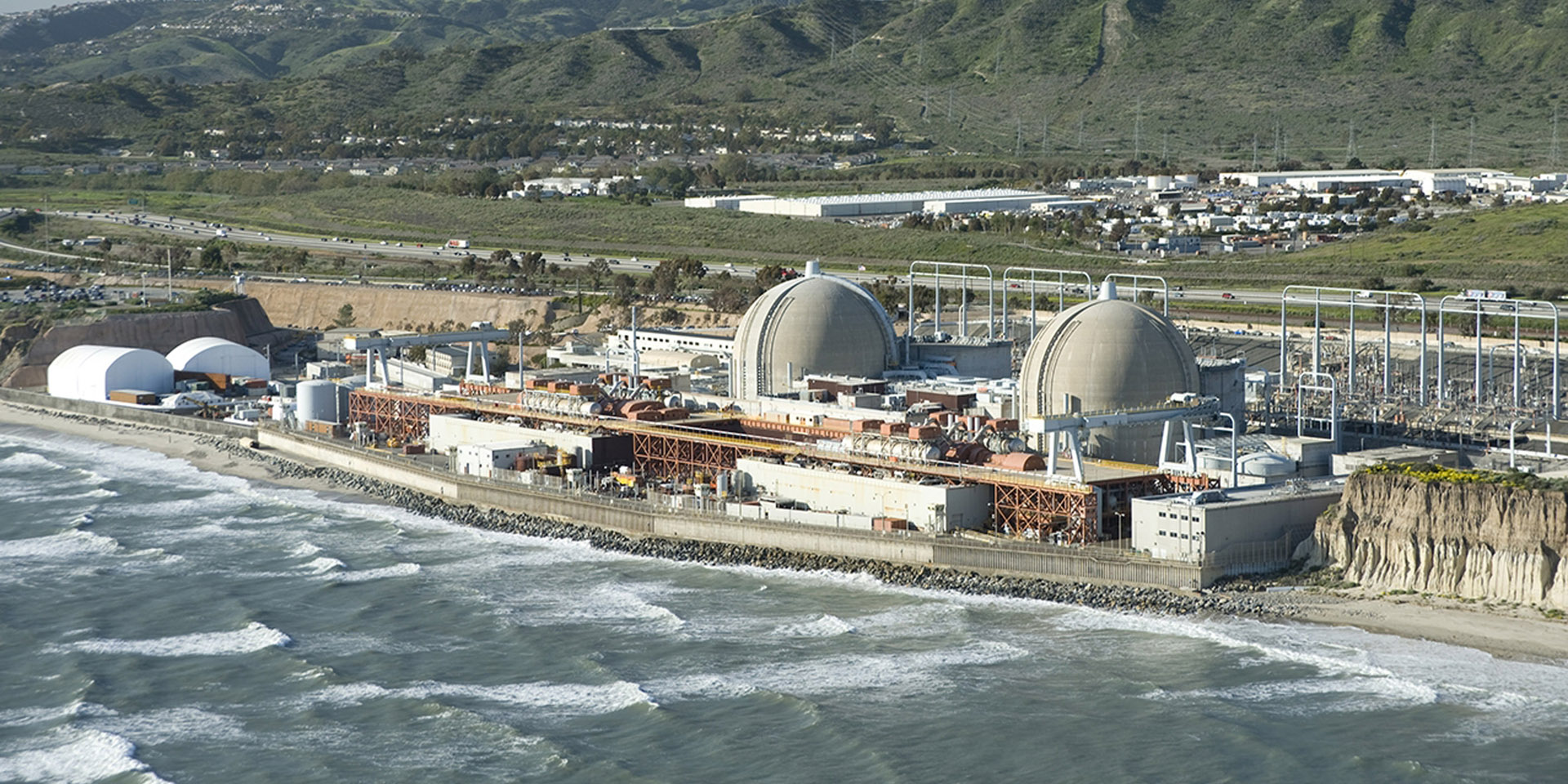
San Onofre Nuclear Generating Station. (Photo: Southern California Edison)
Ten years ago this month, on June 7, 2013, Southern California Edison (SCE) communicated the decision to permanently shutter the San Onofre Nuclear Generating Station (SONGS). The decision set in motion the decommissioning of a plant that had provided steady baseload power for the region since 1968 during a period of tremendous growth in the western United States. In the end, issues presented by the planned replacement steam generators that were intended to support future plant operations proved too large of a hurdle, and the plant was forced to retire.
Westinghouse chief executive officer Patrick Fragman meets with Dominion Energy CEO Bob Blue on May 15 in Washington, D.C. (Photo: Westinghouse)
Westinghouse Electric Company has signed a contract with Dominion Energy to design, manufacture, and deliver replacement steam generators for Virginia’s Surry plant, the nuclear technology firm announced Tuesday.
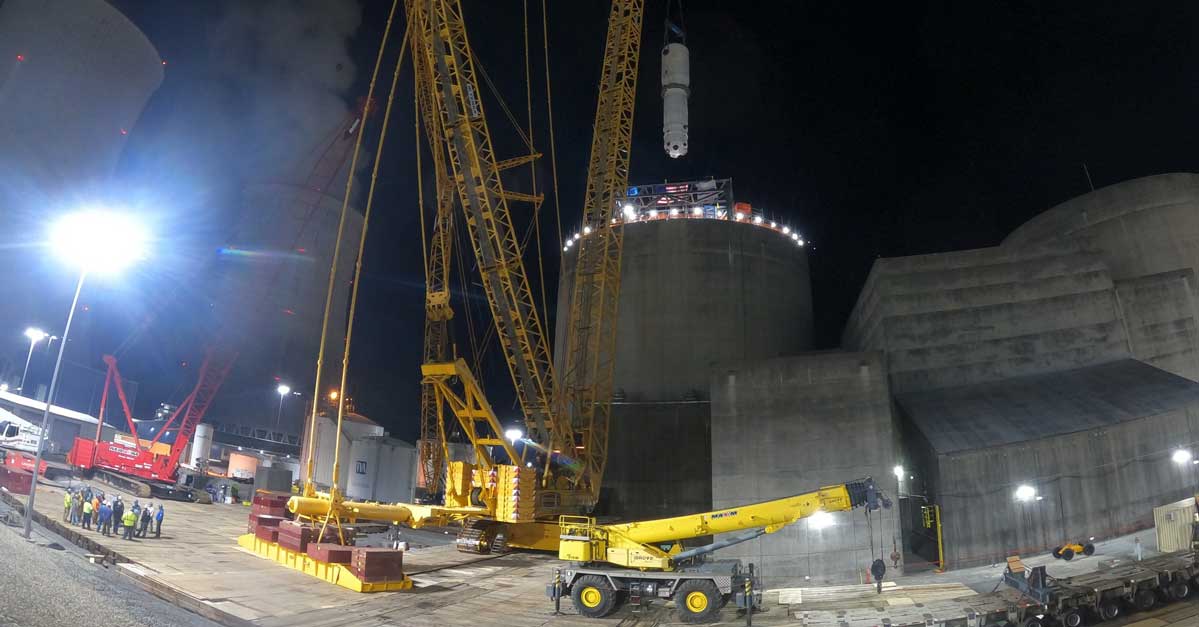
A steam generator is lifted into Watts Bar Unit 2. (Photo: Framatome)
The Steam Generating Team (SGT)—a joint venture of Framatome and United Engineers & Constructors Inc.—has completed a project to replace the Unit 2 steam generators at the Watts Bar nuclear plant, Framatome announced last week.
Watts Barr’s owner and operator, the Tennessee Valley Authority, awarded Framatome the contract for the work in early 2020.
Reactor operators in the control room at Kursk I-1, as the unit is powered down for good. (Photo: Rosenergoatom)
After 45 years of producing electricity, the first unit at Russia’s Kursk nuclear power plant has been retired, plant operator Rosenergoatom announced on Monday. Kursk I-1, one of the facility’s four 925-MWe light water–cooled graphite-moderated reactors, model RBMK-1000 (a Chernobyl-type reactor), was permanently shut down at 00:24 Moscow time on December 19.
Bruce nuclear power plant in Ontario, Canada. (Photo: Bruce Power)
The first of eight 160-ton steam generators for Unit 6 at Canada’s Bruce nuclear power plant was installed last week as part of the facility’s major component replacement project. “Congrats to the MCR team and our partners, including @AeconGroup, @Framatome_CA, @UEandC, @mammoetglobal, @BWXT, and others who contributed to this historic moment,” Bruce Power tweeted on September 30.
The component was fabricated at BWXT Canada’s Cambridge, Ontario, location and was shipped to the Bruce site in late 2020, as shown in this video.
The vendor responsible for generator removal is the Steam Generator Replacement Team (SGRT), a 50-50 joint venture between Aecon and the Steam Generating Team, itself a partnership between Framatome and United Engineers & Constructors. In July, Framatome announced that SGRT had been awarded an approximately C$350 million (about $278 million) contract by Bruce Power to replace the steam generators at Units 3 and 4.
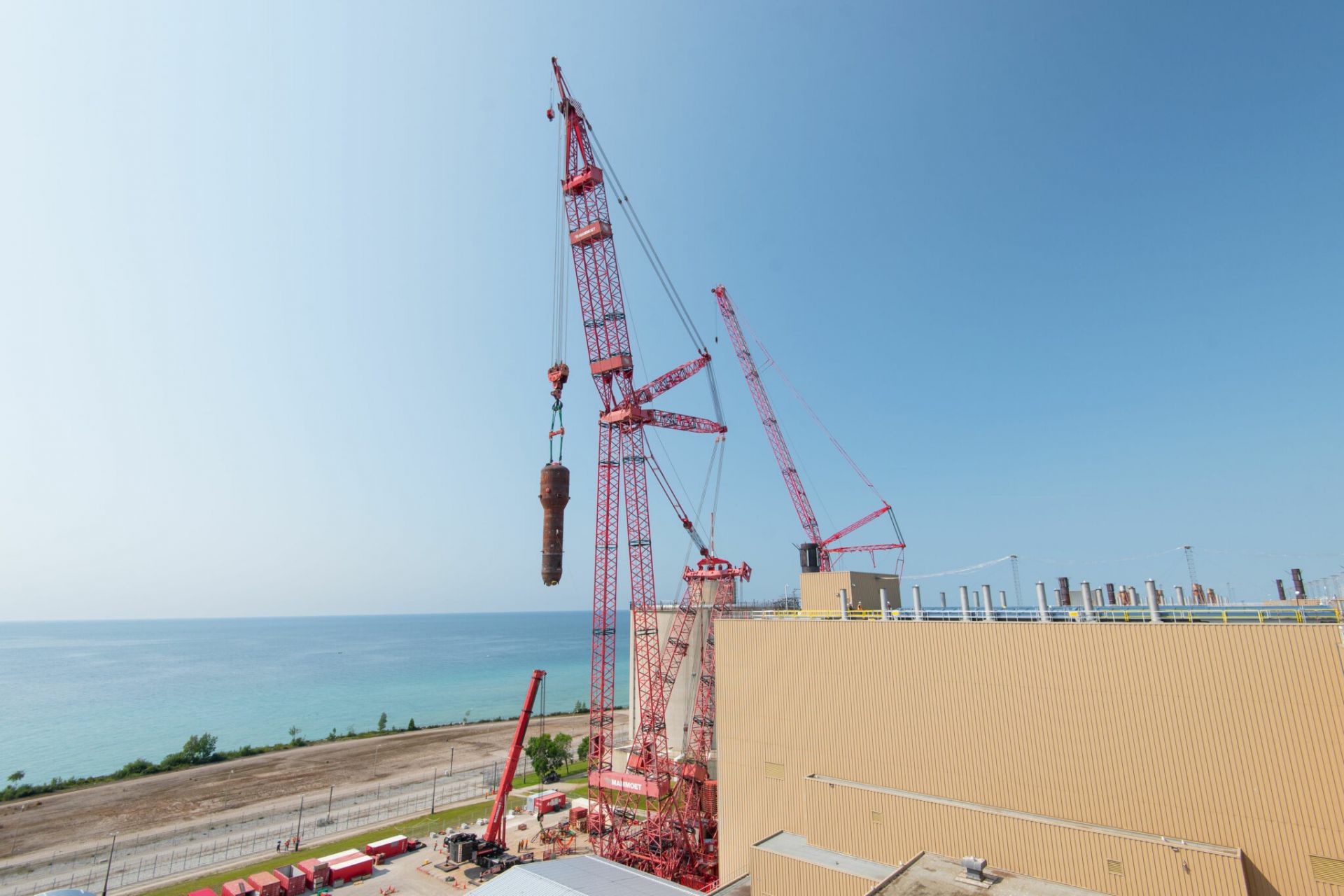
A crane removes the first of the Unit 6 steam generators on July 23. (Photo: Bruce Power)
Bruce Power has removed the first of eight steam generators from Unit 6 at the Bruce nuclear plant in Ontario, the company announced earlier this week. The work was done as part of the facility’s major component replacement (MCR) project.
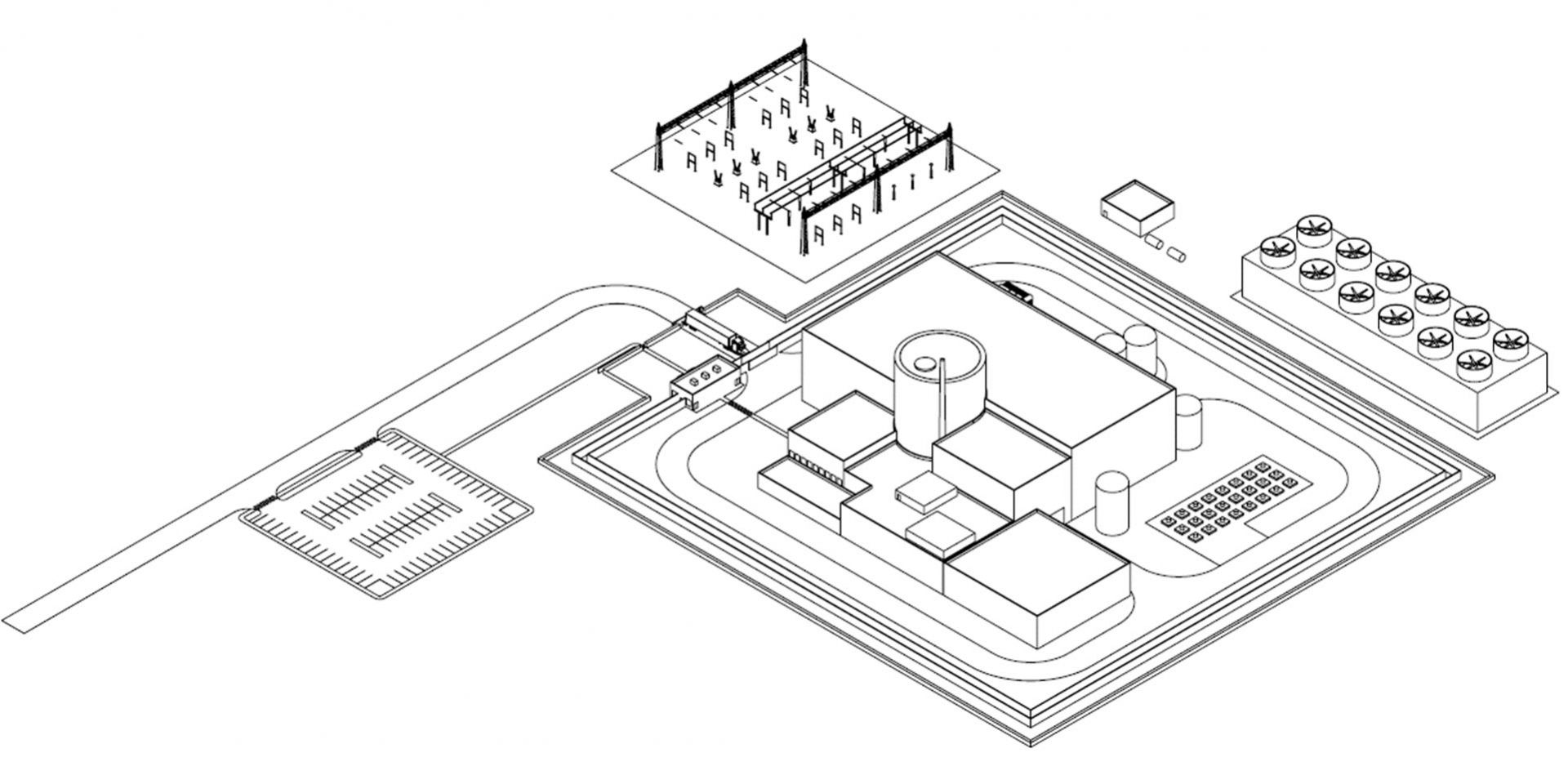
Fig. 1: The layout of a typical SMR-160 site.
Holtec International’s SMR-160 is a pressurized light-water thermal spectrum reactor that relies on natural circulation, thereby eliminating the need for reactor coolant pumps during normal operation. The reference design incorporates a lower pressure conventional steam turbine and wet cooling via a tube-and-shell condenser coupled with forced-draft cooling towers. Optionally, the plant can use dry cooling via Holtec’s HI-KOOL air-cooled condenser.